Knowing about your computer’s Processor (CPU) is important because it is one of the most crucial components of your computer that affects its overall performance similar to Graphic Card details. The CPU is responsible for carrying out all the instructions that your computer receives, and it is the brain of the system. Some of the reasons why you should know about your computer’s Processor (CPU) include:
Table of Contents
- Performance: The CPU’s clock speed and number of cores affect your computer’s processing power, which can impact its overall performance. A more powerful CPU can run applications and software faster, allowing for smoother multitasking and improved performance.
- Compatibility: Certain software and applications require a specific CPU or a minimum processing power to function properly. Knowing the specifications of your CPU will help you determine if your computer can run a particular program.
- Upgrading: If you want to upgrade your computer’s CPU, you need to know the type of socket and other technical specifications to ensure compatibility. Upgrading your CPU can improve your computer’s performance and extend its lifespan.
- Troubleshooting: Knowing your CPU’s specifications can help diagnose problems or performance issues with your computer. For example, if your computer is running slow, checking the CPU usage can help you identify if the CPU is the bottleneck or if there is another issue.
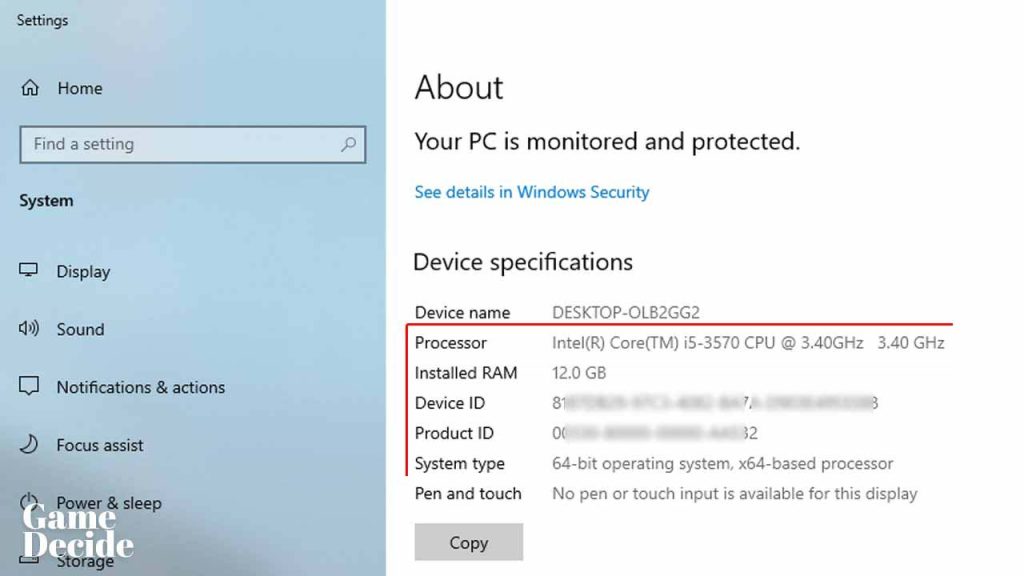

How to check your Processor (CPU) on Windows?
To check your computer’s Processor (CPU), you can follow these steps:
- Open the Windows Start menu by clicking the Windows button on your keyboard or by clicking the Start button in the bottom left corner of your screen.
- Type “system information” in the search bar and click on the “System Information” app that appears in the search results.
- In the System Information window, look for the “Processor” entry under the System Summary section. This entry will list the manufacturer, model, and speed of your CPU.
Alternatively, you can check your CPU using the Windows Task Manager. To do this, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Windows taskbar and select “Task Manager” from the menu.
- In the Task Manager window, click on the “Performance” tab.
- Look for the “CPU” section, which will display the model and speed of your CPU.
You can also check your CPU specifications using third-party software, such as CPU-Z or Speccy. These programs provide detailed information about your computer’s hardware, including the CPU.
By following these steps, you can check your computer’s Processor (CPU) and get information about its specifications, including its manufacturer, model, clock speed, and number of cores.
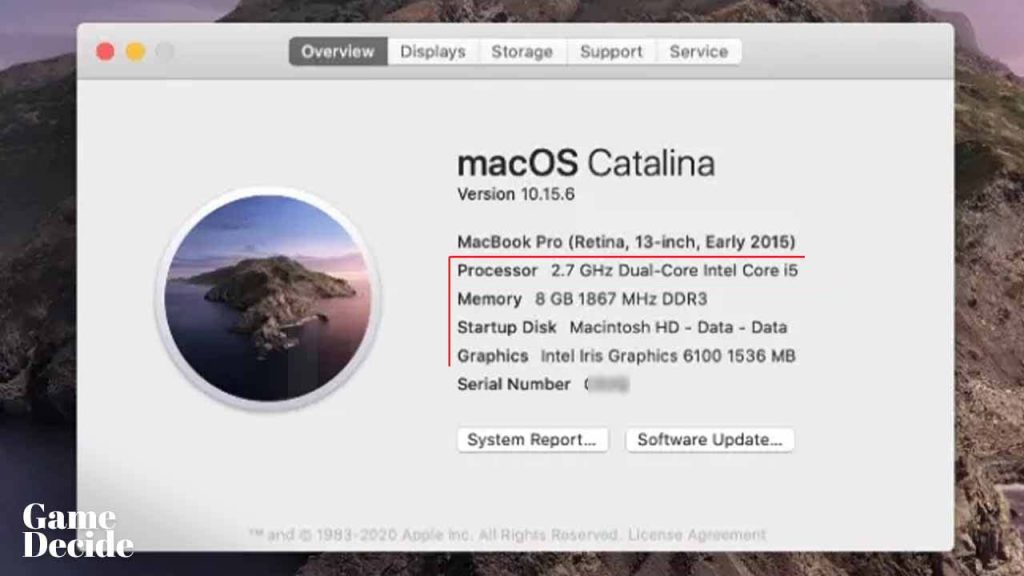

How to check your computer Processor (CPU) on macOS?
To check your computer Processor (CPU) on macOS, you can follow these steps:
- Click on the Apple logo in the top left corner of your screen.
- Select “About This Mac” from the dropdown menu.
- In the “About This Mac” window, click on the “Overview” tab.
- Look for the “Processor” entry, which will list the type, speed, and number of cores of your CPU.
Alternatively, you can check your CPU specifications using the Activity Monitor app. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the Applications folder in Finder.
- Open the Utilities folder.
- Double-click on the “Activity Monitor” app.
- In the Activity Monitor window, click on the “CPU” tab.
- Look for the “CPU Usage” section, which will display the type and speed of your CPU.
You can also use third-party software, such as iStat Menus or Macs Fan Control, to check your CPU specifications and get detailed information about your computer’s hardware.
By following these steps, you can easily check your computer Processor (CPU) on macOS and get information about its specifications, including its type, speed, and number of cores.
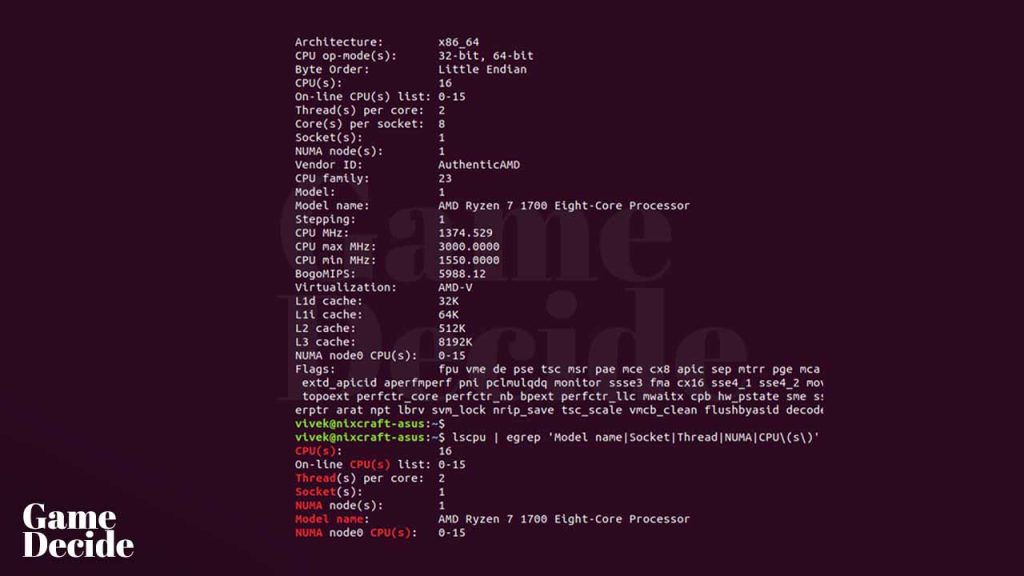

How to check your computer Processor (CPU) on Linux?
To check your computer Processor (CPU) on Linux, you can follow these steps:
- Open the Terminal by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+T keys together.
- Type the following command in the terminal and press Enter:
lscpuThis command will display detailed information about your computer’s CPU. - Look for the “Model name” entry, which will list the model of your CPU.
- You can also check the number of cores and threads, clock speed, cache size, and other specifications of your CPU in the output of the lscpu command.
Alternatively, you can use the System Monitor app to check your CPU specifications. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the System Monitor app by searching for it in the Applications menu.
- In the System Monitor window, click on the “Resources” tab.
- Look for the “CPU History” section, which will display the type and speed of your CPU.
You can also use third-party software, such as CPU-Z or Hardinfo, to check your CPU specifications and get detailed information about your computer’s hardware.
By following these steps, you can easily check your computer Processor (CPU) on Linux and get information about its specifications, including its model, clock speed, cache size, and number of cores and threads.
FAQ’s
Here are some frequently asked questions and answers about Processor (CPU):
What is a CPU?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, which is the primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing tasks. It is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer.
What are the key specifications of a CPU?
The key specifications of a CPU include the number of cores, clock speed (measured in GHz), cache size, and thermal design power (TDP). These specifications determine how fast and efficiently the CPU can perform tasks.
What is a CPU core?
A CPU core is a processing unit within the CPU that can perform tasks independently. A CPU with multiple cores can perform multiple tasks simultaneously, which can result in better performance.
What is CPU clock speed?
CPU clock speed, also known as clock rate, is the frequency at which the CPU executes instructions. It is measured in gigahertz (GHz).
What is CPU cache?
CPU cache is a small amount of high-speed memory that is built into the CPU. It is used to temporarily store frequently accessed data and instructions, which can speed up the CPU’s performance.
What is TDP?
TDP stands for Thermal Design Power, which is the maximum amount of heat that a CPU can generate under normal operating conditions. It is measured in watts (W) and can help determine the CPU’s power consumption and cooling requirements.
How do CPU specs affect performance?
CPU specs such as the number of cores, clock speed, cache size, and TDP can all affect the CPU’s performance. CPUs with more cores and higher clock speeds can perform tasks faster and more efficiently, while larger caches can improve performance for certain tasks. TDP can also affect performance indirectly by determining the CPU’s power consumption and cooling requirements.
What is CPU overheating, and how can it be resolved?
CPU overheating occurs when the CPU temperature exceeds its maximum operating limit, which can cause the computer to slow down or even shut down. To resolve this issue, you can clean the CPU fan and heatsink, apply new thermal paste, ensure proper airflow in the computer case, or even upgrade the CPU cooling system.
What is CPU bottlenecking and how can it be resolved?
CPU bottlenecking occurs when the CPU is unable to keep up with the demands of other components in the computer, such as the graphics card. This can result in reduced performance and lower frame rates in games or other applications. To resolve this issue, you can upgrade the CPU to a faster model or adjust the settings of the application to reduce its demands on the CPU.
What is CPU throttling, and how can it be resolved?
CPU throttling occurs when the CPU automatically reduces its clock speed or performance to prevent overheating or power consumption. This can result in reduced performance in some applications. To resolve this issue, you can adjust the CPU power settings in the computer’s BIOS or operating system to allow for higher performance, or upgrade the CPU cooling system.
What is CPU compatibility, and how can it be checked?
CPU compatibility refers to whether a particular CPU is compatible with the motherboard and other components in the computer. To check CPU compatibility, you can consult the motherboard manual or manufacturer’s website to find the list of compatible CPUs, or use online tools such as PCPartPicker to ensure compatibility before purchasing a new CPU.
What is CPU failure, and how can it be diagnosed?
CPU failure can occur due to various reasons such as overheating, power surges, or physical damage. Symptoms of CPU failure can include a computer that won’t turn on or crashes frequently. To diagnose CPU failure, you can perform a CPU stress test or run diagnostic software to check for errors or faults in the CPU.
If you have a question feel free to ask in the comments.






